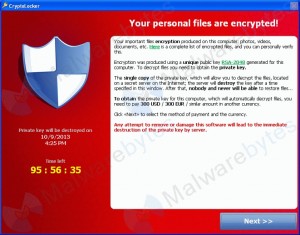
I had a telephone call from a former client a month or so ago. He was in a bit of a panic because he was suffering from the Google “red screen of doom”. Having been in IT for a while I’m familiar with Microsoft’s “blue screen of death” but this was something that was new to me, or so I thought and so I asked for more information.
He asked me to do a search for his company on Google – which I did – and his company came top of the search results, which was good. What was less good – much less good – was the stark warning, inserted by Google, that “This site may harm your computer” .
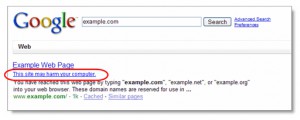 Aha, Google was warning that the website had been hacked and was now serving malware to visitors.
Aha, Google was warning that the website had been hacked and was now serving malware to visitors.
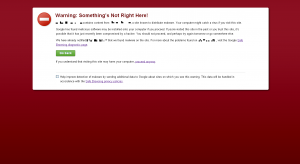
I switched to my Chromebook – which is impervious to all known computer malware – and clicked through to the website – only to be blocked by the “Google red screen of doom”
 Although there was nothing to buy on my client’s site, it did host a range of technical papers and specification sheets that were vital for his clients and this attack was already having an impact on his business. Action was desperately needed.
Although there was nothing to buy on my client’s site, it did host a range of technical papers and specification sheets that were vital for his clients and this attack was already having an impact on his business. Action was desperately needed.
The site was originally built 7 years ago and nothing much had changed, including the access data required to log-in to the host. So, I logged in and saw that a number of .js files had newer dates on them than the rest of the content, confirming that the site had been hacked and a small number of files altered so that they could be used to force malware downloads on to the computers of unsuspecting visitors.
The next step was to delete all of the website files, just to be on the safe side, and create a new, simple, home page with contact details and links to the most popular PDFs so that clients would be able to access the information they required.
Next was to see what Google had found by logging in to the Google Webmaster Toolkit account for the website- www.google.com/webmaster.
There were a number of warnings relating to suspicious activity on the site that had gone unread, simply because my client had changed email addresses, was unable to access the original email account and had not updated his Webmaster Tools account with the new address.
Webmaster Tools advised of the type of threat that had been set up on the site and provided other, valuable, information along with a reporting tool that enabled me to advise Google of the actions taken to remove the threat.
Clicking “Send” was quickly followed by a confirmation message from Google that they would look at my message within 18 hours – a time frame that I thought was commendably fast. They were as good as their word and within 18 hours had checked the website to make sure it was clean and had removed all warnings and red screens of doom – my client was back up and running.
However, we didn’t leave it there. The original site was old, used old code and the web hosts weren’t the most responsive – telephone calls to their support line either went unanswered or, when answered, were as much use as the proverbial chocolate teapot and so the decision was made to move the hosting to a more secure provider and to work on a plan to develop a new website.
The moral of this tale is simple. Make sure that you use the Google Webmaster Toolkit!
It’s the only way to let Google know what you’ve done should your site fall victim to an attack, keep your Toolkit account up to date and only use a web host that you know provides good security and a decent level of support.
And please don’t think that you’re immune – small businesses are the most targeted, the presumption being that their security is weaker than measures put in place by larger organisations and there are a number of websites that I keep an eye on that are attacked many times a day. However, being hosted on a secure platform with monitoring in place means that I am kept aware of the threats and can take remedial action, if required, very quickly.
To date, none has been required.
If you are worried by the security of your website, or your IT systems, please give me a call on 01793 238020 or email me, andy@enterprise-oms.co.uk for a confidential, impartial, and free chat about your security concerns