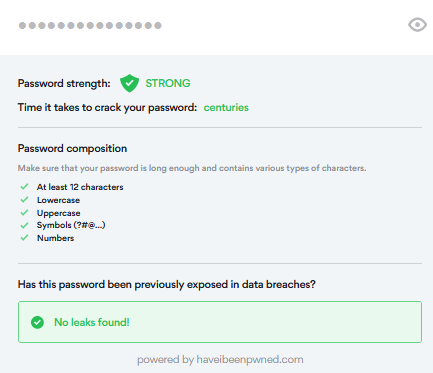
In today’s interconnected digital world, Solopreneurs, sole traders, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) face an increasing number of cyber threats that can have severe consequences for their operations, reputation, and financial stability. Cybersecurity has become a critical aspect of business management for all businesses as they are often targeted by cybercriminals seeking to exploit their vulnerabilities. Vulnerabilities that are easier for the cybercriminals to take advantage of than in larger companies that have dedicated cyber security teams. This article explores the importance of cybersecurity for SMEs, highlighting the risks they face and the measures they should take to protect themselves.
Growing Cybersecurity Threats:
Small businesses and Sole Traders are an attractive target for cybercriminals. This is due to their limited resources, inadequate security infrastructure, and lack of awareness. This makes them a very profitable target for Cyber attacks such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing scams, and social engineering opportunities. All of these are on the rise, and SMEs are increasingly falling victim to these malicious activities. The financial and reputational damage resulting from such incidents can be devastating for a small business.
Financial Implications:
Cyberattacks can lead to significant financial losses for SMEs. Data breaches can result in the loss of sensitive customer information, leading to legal repercussions, fines, and lawsuits. The cost of recovering from a cyberattack, including investigation, remediation, and system restoration, can be exorbitant for SMEs with limited budgets. Additionally, businesses may experience a loss of customer trust, impacting future sales and long-term growth.
Reputational Damage:
The reputation of an SME is a valuable asset that can take years to build but can be destroyed in an instant due to a cyber incident. A breach of customer data or a successful hacking attempt can tarnish a company’s reputation, resulting in decreased customer loyalty and damaged relationships with stakeholders. Rebuilding trust and recovering from reputational damage can be a challenging and time-consuming process for SMEs.
Compliance and Legal Requirements:
SMEs must comply with various data protection and privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and industry-specific requirements. Failure to meet these obligations can lead to severe penalties and fines. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is crucial for SMEs to ensure compliance with these regulations, protecting both their customers’ data and their own legal standing.
Competitive Advantage:
Investing in cybersecurity can provide SMEs with a competitive edge in today’s business landscape. Many customers prioritize security when choosing a service or product provider. By demonstrating a strong commitment to protecting customer data and maintaining secure operations, SMEs can build trust with potential clients and gain a competitive advantage over less secure competitors.
One of the most effective ways of demonstrating cyber security to the outside world is through the Cyber Essentials schemes where businesses that can demonstrate their cyber security are provided with a certificate that proves their cyber security credentials to existing and potential customers
Supply Chain Risks:
SMEs are often part of complex supply chains, working closely with other businesses. Weak cybersecurity measures within an SME can create vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals to gain access to larger organizations. A breach in one link of the supply chain can have a cascading effect, affecting multiple businesses. Therefore, SMEs must prioritize cybersecurity not only for their own protection but also to ensure the security of their partners and customers. Many large organisations often demand proof of good Cyber security practices and the Cyber Essentials program is a good way to demonstrate this
Employee Awareness and Training:
Employees play a crucial role in maintaining cybersecurity within an organization. SMEs should invest in cybersecurity awareness and training programs to educate their employees about best practices, common threats, and how to respond to potential incidents. By fostering a culture of cybersecurity, SMEs can empower their employees to be proactive in identifying and mitigating cyber risks.
Proactive Cybersecurity Measures:
SMEs can take several proactive measures to enhance their cybersecurity posture. Implementing strong password policies, regularly updating software and systems, utilizing multi-factor authentication, encrypting sensitive data, and regularly backing up critical information are some essential steps. It is also advisable to invest in reliable antivirus software, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to protect against external threats.
Collaboration
Collaboration and External Support: SMEs can benefit from collaborating with cybersecurity experts, industry associations, and government agencies. These partnerships can provide valuable insights, guidance, and resources to help SMEs strengthen their cybersecurity defences. Engaging with third-party cybersecurity providers can also offer specialized expertise and solutions tailored to the specific needs and budget constraints of SMEs.
Continuity and Disaster Recovery Planning:
SMEs should develop comprehensive continuity and disaster recovery plans to ensure business operations can quickly resume in the event of a cyber incident. Regularly backing up data, testing backup and recovery processes, and establishing redundant systems are vital components of such plans. By preparing for potential disruptions, SMEs can minimize downtime and mitigate the financial and operational impact of cyberattacks.
Ongoing Risk Assessment and Adaptability:
Cybersecurity is not a one-time effort but requires continuous monitoring, risk assessment, and adaptation. SMEs should regularly evaluate their cybersecurity measures, identify vulnerabilities, and implement necessary updates or upgrades. As technology and cyber threats evolve, SMEs must stay informed about emerging risks and adopt proactive measures accordingly.
Building Customer Trust:
Strong cybersecurity practices help SMEs build trust with their customers. By prioritizing data protection and privacy, SMEs can assure their clients that their information is safe and secure. This trust can result in increased customer loyalty, positive word-of-mouth recommendations, and repeat business, contributing to long-term success and growth.
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity is of paramount importance to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in today’s digital landscape. The increasing prevalence of cyber threats and the potential financial, reputational, and legal consequences emphasize the need for robust cybersecurity measures. By investing in cybersecurity, SMEs can protect their sensitive data, maintain customer trust, comply with regulations, gain a competitive advantage, and ensure the continuity of their business operations. Through proactive measures, collaboration with experts, and a focus on employee training, SMEs can mitigate cyber risks and safeguard their future in an increasingly interconnected world.
If you need help with your Cyber Security I can help and can even point you in the direction of a really excellent Cyber Security company if you need more in-depth help and support.
Get in touch – even if it’s just for a free consult. You can call me on 01793 238020 or 07966 547146, email andy@enterprise-oms.co.uk or book a slot using my calendar and we’ll take it from there